Introduction to ESG
Definition
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) refers to a set of criteria used to assess a company's performance and impact on environmental, social and governance aspects.
What's the difference with sustainability?
Sustainability is a broader concept that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It concerns a broader spectrum of human activities, including public policies, individual behavior and community strategies.
Although ESG and sustainability are interconnected, ESG is more specific to investment and business management practices, while sustainability encompasses a broader vision of balanced long-term development for society as a whole.
Importance of ESG
ESG criteria are essential for investors and companies alike, as they help identify non-financial risks and opportunities, thereby improving long-term performance and reputation.
Legal framework, Standards and Reference systems
Legal obligations
The legal framework for ESG is complex and varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, but is increasingly influenced by international and regional initiatives. The European Union requires large companies to publish information on how they manage social and environmental issues. From 2024, the framework will be progressively extended under the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive).
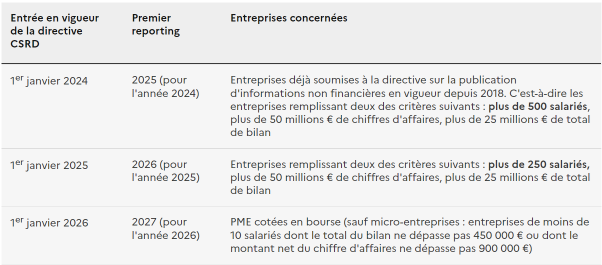
Application of the directive in 3 stages - Official French Government website for administrative information and procedures for businesses
This means that companies must comply with the ESRS (European Sustainability Reporting Standards).
- Auditing by a statutory auditor
- Quantitative (CO2 balance) and qualitative assessment
- Evaluation of the methods used
- If information excluded -> justify
- Follow-up of results over time with achievement of objectives
- Content of the standardized report
- Valuation across the entire value chain...
... so it also applies to SMEs
In Switzerland, obligations differ for the time being. So-called public-interest companies (banks, insurance companies) are required to publish certain non-financial information in accordance with Art. 964 of the Swiss Code of Obligations. The Federal Council opened a consultation at the end of June 2024 to transpose the CSRD into Swiss law. The same duties and obligations apply to companies.
Voluntary Initiatives and Standards
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
- Provides a framework for disclosing the economic, environmental and social impact of companies.
- Used by thousands of organizations worldwide to improve transparency and accountability.
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
- Develops disclosure standards to help companies communicate their ESG performance more effectively to investors.
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
- Provides recommendations for improving disclosure of climate-related financial risks.
ISO 26000
- International standard providing guidelines for corporate social responsibility.
ESG criteria
Themes according to CSRD
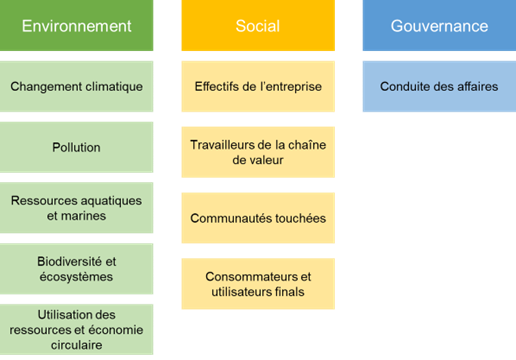
Examples of KPIs
- Environment :
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Energy consumption due to own operations
- Renewable energy production
- Percentage of net income from oilfield customers
- Air pollutant emissions
- Total water consumption
- Quantity of special waste
- Social
- Number of employees by type
- Percentage of turnover
- Percentage self-employed
- Gender distribution in management
- Training hours per employee
- Equal pay
- Number of customer complaints
- Data security management
- Governance
- Number of employees represented on the Board of Directors
- Total fines for corruption
- Donations to political parties or lobbies
- Payment methods
- Local suppliers
- Late payment rate
Steps for implementing an ESG approach
- Define the scope
- Identify stakeholders and the value chain
- Analysis according to the dual materiality of finance vs. impact (ESG impacts on the company's development, performance and results vs. impacts of the business on the economic, social and natural environment).
- Define what data to collect
- Collecting and evaluating data
- Setting SMART objectives
- Draw up an action plan to achieve objectives (short, medium and long term)
- Designing the annual report
- Track your progress, improve
